
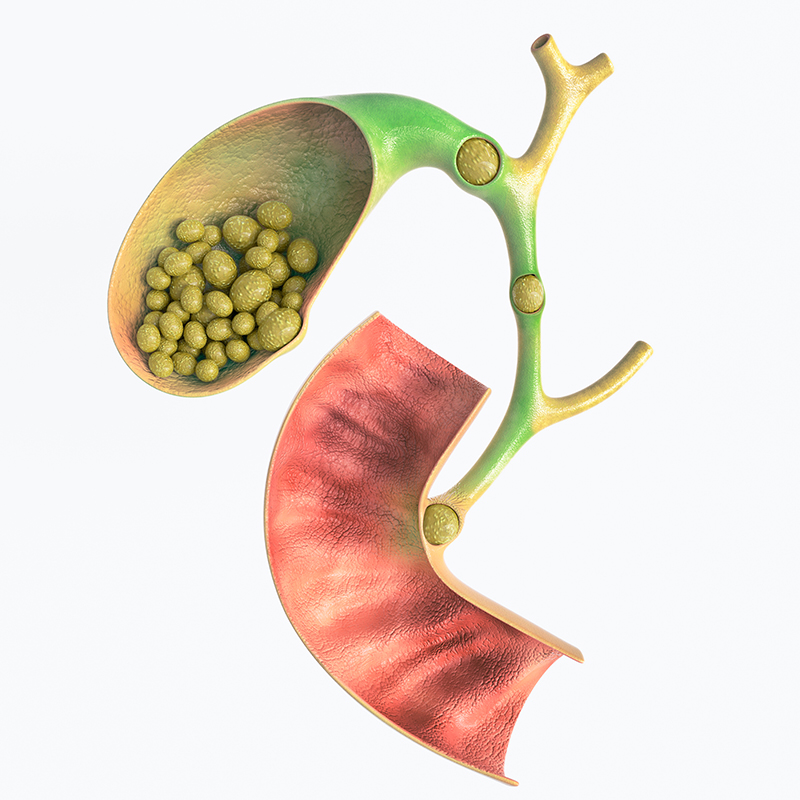
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy-Minimally Invasive Surgery for Gallstones
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid mainly made of cholesterol which is formed in the gallbladder. The prevalence of gallstones is approximately 10-15% in general population. Due to some particular risk factors such as hypercholesterolemia (high level of blood cholesterol), taking medications that contain estrogen such as oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy and having had several children, women age over 40 have greater risk to develop gallstones.
Symptoms of Gallstone/ Cholecystitis:
Signs and symptoms of acute cholecystitis include severe and sudden pain in the upper right or center abdomen, especially when breathing in and out. In severe cases, aggravated symptoms are jaundice presented with a yellow tinge to the skin and whites of the eyes and dark urine, pale stool due to lack of bile salt released into the stool but accumulated in blood. In case of gallbladder ruptures, patient might manifest high fever with chills, nausea and vomiting, pain that spreads to the right shoulder or back and tenderness over the abdomen when it is touched. These symptoms are serious and immediate medical attention is highly needed.
Treatment of cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is normally self-limiting with a complete cure rate within 1-2 weeks. If symptoms show up within a week, gallbladder removal surgery is highly recommended. However, it cholecystitis is presented with its serious complications, antibiotics acting against infections and Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage to open a blocked bile duct will be the treatment options. Nevertheless, treatment plan will be carefully selected by expert physicians based on disease severity, complications and patient’s conditions. In case that symptoms last longer than a week with a good response to treatment, surgery to remove gallbladder might be further advised in the next 6-12 weeks. In the contrary, if there is no or poor treatment response to given medications or presence of sepsis, abscess or gangrene of gallbladder, emergency surgery is highly required.
Gallbladder removal surgery
There are 2 main surgical techniques to remove gallbladder:
1. Open Cholecystectomy: It is conventional approach used to remove gallbladder in cases of severe infection and inflammation or ruptured gallbladder.
2. Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Laparoscopic surgery (laparoscopic cholecystectomy or LC) is a minimally invasive surgery to remove gallbladder which is performed by highly experienced and well-trained surgical team. The procedure involves these steps:
 Small incisions (each one inch or less in length) are made in the abdominal and umbilical areas instead of making an open large cut in the abdomen.
Small incisions (each one inch or less in length) are made in the abdominal and umbilical areas instead of making an open large cut in the abdomen.
 The surgical instruments are inserted via these small incisions such as a laparoscope, a narrow tube with a camera. This allows surgeons to clearly visualize all dimensions of gallbladder on a screen before having it removed accurately and safely.
The surgical instruments are inserted via these small incisions such as a laparoscope, a narrow tube with a camera. This allows surgeons to clearly visualize all dimensions of gallbladder on a screen before having it removed accurately and safely.
 Gallbladder will be then removed safely from the liver.
Gallbladder will be then removed safely from the liver.
After procedure is completely done, the surgical incisions will be properly closed and sealed. Due to smaller incisions, it results in less pain, fewer post-operative complications, faster recovery time and shorter hospital stay. In healthy surgical candidates, post-operation, patients can walk within 4-6 hours and average length of hospital stay is 1-2 days. Patients can return to daily life and activities even quicker.
Successful clinical outcomes of laparoscopic cholecystectomy
 100% Performed by highly skilled surgical and multidisciplinary team.
100% Performed by highly skilled surgical and multidisciplinary team.
 100% Patient’s ability to walk within 4-6 hours after operation * in healthy candidates for surgery.
100% Patient’s ability to walk within 4-6 hours after operation * in healthy candidates for surgery.
 93% Success rate of operation incluing in acute cholecystitis
93% Success rate of operation incluing in acute cholecystitis
 0 % Major injury of bile duct.
0 % Major injury of bile duct.
 0 % Post-operative infections *in patients without cholecystitis.
0 % Post-operative infections *in patients without cholecystitis.
Reference: Statistical data obtained from Surgery Center, Bangkok Hospital 2018
Reference:
Dr. Chanin Pundee
Surgeon (laparoscopic and endoscopic surgery), Surgery Center, Bangkok Hospital.